China’s Real Estate Crisis: The Catalyst of Market Struggles
China, the world’s largest steel producer and consumer, plays a pivotal role in shaping global steel trends. Its ongoing real estate downturn has sent shockwaves through the steel sector. The collapse of property giants like Evergrande and Country Garden has led to decreased construction activity, a primary driver of steel consumption.
According to Credendo, the Chinese real estate market, which contributes nearly 40% of the country’s steel demand, has been struggling under immense debt and declining sales. New property construction has slowed significantly, with investments in the sector dropping by 12% year-on-year as of late 2024.
The prolonged downturn has led to a substantial decline in steel consumption. Chinese demand for hot-rolled coil (HRC) and other steel products has waned, forcing domestic producers to cut prices in an attempt to clear inventories. Export prices for Chinese steel products also fell, intensifying competition in global markets.
China’s Real Estate Crisis: The Catalyst of Market Struggles
China, the world’s largest steel producer and consumer, plays a pivotal role in shaping global steel trends. Its ongoing real estate downturn has sent shockwaves through the steel sector. The collapse of property giants like Evergrande and Country Garden has led to decreased construction activity, a primary driver of steel consumption.
According to Credendo, the Chinese real estate market, which contributes nearly 40% of the country’s steel demand, has been struggling under immense debt and declining sales. New property construction has slowed significantly, with investments in the sector dropping by 12% year-on-year as of late 2024.
The prolonged downturn has led to a substantial decline in steel consumption. Chinese demand for hot-rolled coil (HRC) and other steel products has waned, forcing domestic producers to cut prices in an attempt to clear inventories. Export prices for Chinese steel products also fell, intensifying competition in global markets.
Global Steel Prices Under Pressure
The ripple effects of China’s real estate crisis are felt across the global steel market. Steel prices have come under significant pressure due to oversupply and subdued demand.
Steel Prices in Decline
As reported by The Edge Markets Malaysia, global steel prices have softened due to weak demand in key markets. In November 2024, hot-rolled coil (HRC) prices dropped by 4% month-on-month in China, with similar trends observed in Europe and the US.
The problem is further exacerbated by high production levels in China. Despite the weak market conditions, Chinese steelmakers continue to operate at near-record capacity, adding to the global oversupply and depressing prices further.

Regional Market Impacts
- Europe: The European steel market has faced declining apparent consumption, compounded by rising energy costs and stagnant industrial growth. Steel prices in Europe remain volatile, with subdued demand from the automotive and construction sectors.
- United States: Steel shipments in the US fell by 4% year-on-year in the first nine months of 2024, reflecting a broader trend of weak domestic demand. Rising import costs due to geopolitical factors and tariff barriers have also complicated the market.
- Asia-Pacific: Beyond China, other Asia-Pacific markets are struggling to adapt to fluctuating raw material prices and shifting trade patterns.
Structural Challenges in the Steel Industry
The steel sector’s woes go beyond cyclical demand fluctuations. Structural issues such as rising energy costs, tightening environmental regulations, and supply chain disruptions pose additional challenges.
Environmental Pressures
Governments worldwide are pushing the steel industry to decarbonize, requiring heavy investments in green technologies like hydrogen-based steelmaking and electric arc furnaces. While these initiatives align with global climate goals, they also impose financial burdens on steel producers.
Rising Energy Costs
In Europe, energy prices surged in late 2024, impacting steel production costs. For instance, natural gas prices in the region rose by 10.2% month-on-month in November. This has made European steel less competitive on the global stage compared to regions with lower energy costs.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Geopolitical tensions and trade restrictions have disrupted the flow of raw materials like iron ore and coking coal, further straining the industry. Countries like Australia and Brazil, major exporters of these resources, have experienced logistical challenges, leading to price volatility.
China’s Real Estate Downturn: A Key Catalyst
China’s real estate sector, accounting for nearly 40% of the country’s steel demand, has seen a dramatic slowdown. New construction starts in the first half of 2024 declined by approximately 24%, continuing a multi-year trend of contraction. The collapse of major property developers like Evergrande and Country Garden has further compounded the issue, with projects delayed and confidence in the sector waning.
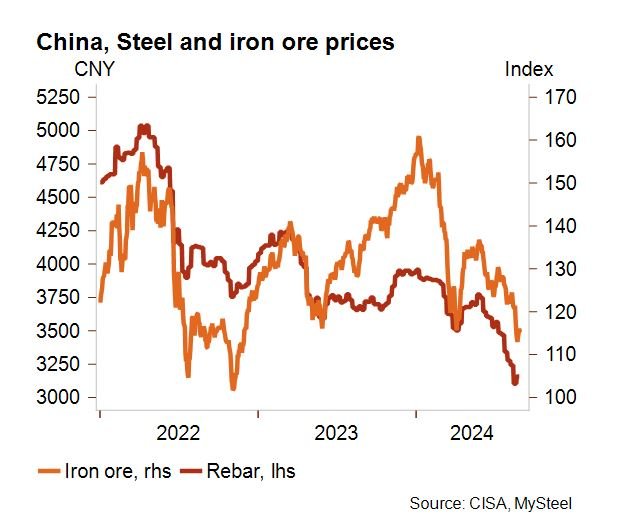
This sustained downturn has decimated steel demand in the construction sector, leading to an oversupply. To balance the market and stabilize prices, many steel mills in China are reducing production. However, these measures are unlikely to fully offset the surplus, as the time lag between land purchases and construction projects limits immediate recovery prospects.
Global Steel Prices Under Pressure
The oversupply of steel in China has sent shockwaves through the global market, pushing prices down.

Decline in Steel and Iron Ore Prices
Iron ore, a critical raw material for steel production, has seen its prices fall below the USD 100-per-tonne mark. This drop reflects weak demand from Chinese steel mills and high inventory levels at ports, which grew by 31% in 2024. Major iron ore exporters like Australia and Brazil have slowed shipments, while global miners such as BHP and Rio Tinto are grappling with reduced profits.
In parallel, Chinese steel prices have plummeted. Rebar prices are at their lowest since 2017, and hot-rolled coils have hit a four-year low. Many producers, particularly those with higher operating costs, are now operating at a loss, exacerbating the financial strain on the sector.
Impact on Global Markets
The decline in Chinese steel prices has intensified competition in international markets. In 2024, China’s steel exports surged to their highest level in eight years, flooding foreign markets with low-cost products. This aggressive export strategy has disrupted local industries worldwide and triggered trade tensions.
Tariffs and Trade Barriers
To counter the influx of cheap Chinese steel, several countries have imposed tariffs and trade restrictions.
United States
The US raised tariffs on certain steel and aluminum products from 0-7.5% to 25% earlier this year. This move aims to protect domestic producers struggling with the dual challenge of competing against cheaper imports and meeting stricter environmental regulations.
European Union
In the EU, anti-dumping investigations into Chinese steel imports have gained momentum. Policymakers are determined to level the playing field for local producers, who face significant cost disadvantages compared to subsidized Chinese exports.
Latin America
Countries like Mexico, Chile, and Brazil have also raised tariffs to shield their industries. These measures reflect a broader trend of protectionism in response to China’s export strategy.
Energy Transition and Green Steel Challenges
The global push for decarbonization has added another layer of complexity to the steel industry. The transition from fossil fuel-based production to renewable energy-intensive processes is capital-intensive, creating long-term competitive challenges for green steel producers.
Cost Implications
The high costs of retrofitting existing plants to accommodate green technologies like hydrogen-based steelmaking pose significant financial hurdles. Despite government subsidies to bridge the cost gap, green steel remains more expensive than its traditional counterpart, which relies on high-carbon methods.
Market Implications
The reliance on cheaper imports from regions with less stringent environmental regulations undermines efforts to promote green steel. As a result, producers in countries with ambitious climate goals face a dual burden: higher costs and declining competitiveness.
Diverging Trends in Other Metals
Interestingly, the downward trend in steel prices has not extended to all metals.
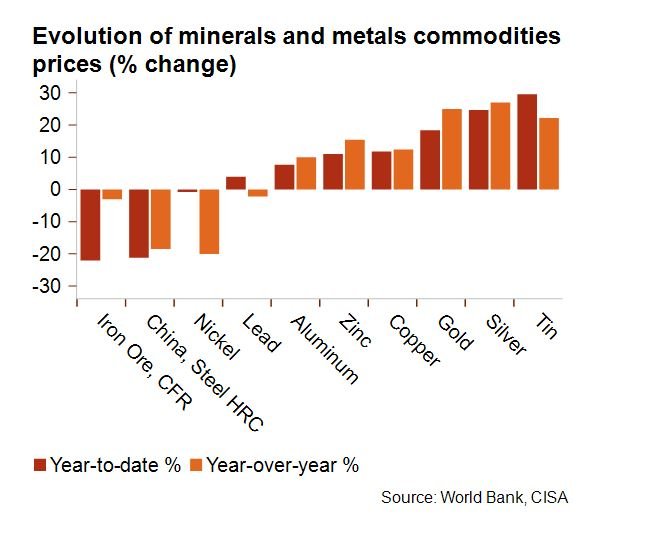
- Aluminum and Copper: Prices for these metals have risen, driven by strong demand in sectors like electronics and renewable energy.
- Nickel: While nickel prices have stabilized after a year-over-year decline, they remain critical for industries such as battery production and stainless steel manufacturing.
Future Outlook: Navigating Challenges and Opportunities
The global steel industry faces a challenging road ahead, but opportunities for growth and innovation remain.
Infrastructure Investment
Infrastructure projects worldwide offer a glimmer of hope. Governments are investing heavily in transportation, energy, and housing, creating potential demand for steel. Emerging markets, in particular, are poised to benefit from these investments.
Shift to High-Tech Industries
China’s government is focusing on developing high-tech industries and boosting consumer spending to offset the decline in real estate demand. While these sectors are less steel-intensive, they represent new avenues for growth.
Green Steel Adoption
The transition to green steel production, while costly, is inevitable as countries adopt stricter climate policies. Producers investing in sustainable technologies today may gain a competitive edge in the long run.
Conclusion
China’s real estate crisis and aggressive steel export strategy have created significant headwinds for the global steel industry. Falling prices, rising trade barriers, and the costly shift toward green production are reshaping the market. The global steel market faces a confluence of challenges, from China’s real estate downturn to rising costs and environmental pressures. However, opportunities in infrastructure development, high-tech industries, and sustainable practices offer a pathway for recovery. As the industry adapts to these challenges, strategic investments and innovation will be key to ensuring resilience and long-term growth.
For more insights and expert perspectives on the steel industry, visit Lux Metal.
References:

