What is a Net-Zero Building?
A net-zero building is one that produces as much energy as it consumes over the course of a year. This is achieved through a combination of energy-efficient design, advanced building materials, and the use of renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power. In some cases, these buildings may even generate more energy than they consume, feeding the excess back into the grid.
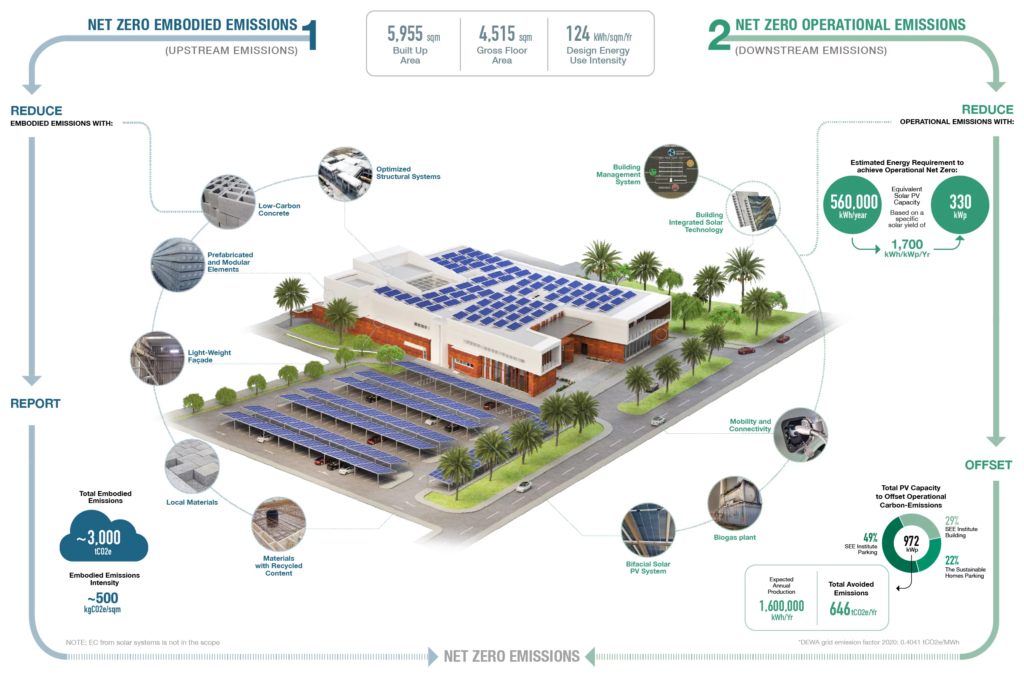
The net-zero concept addresses both energy consumption and carbon emissions. The aim is to minimize a building’s environmental impact while maintaining the functionality and comfort that users expect. Achieving net-zero status requires careful planning at every stage of a building’s lifecycle—from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
The Importance of Sustainability in Construction
The construction industry is traditionally resource-intensive, with a large carbon footprint stemming from the use of non-renewable materials, high energy consumption, and waste generation. According to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), buildings are responsible for nearly 40% of global energy-related carbon emissions. The shift toward sustainable construction practices is thus crucial in mitigating the environmental impact of buildings.
Net-zero buildings play a vital role in this transformation by focusing on sustainability from the outset. These structures are designed to minimize resource consumption and environmental harm while ensuring long-term energy efficiency. In doing so, net-zero buildings help reduce the industry’s dependence on fossil fuels and contribute to global efforts to curb carbon emissions.
How Do Net-Zero Buildings Work?
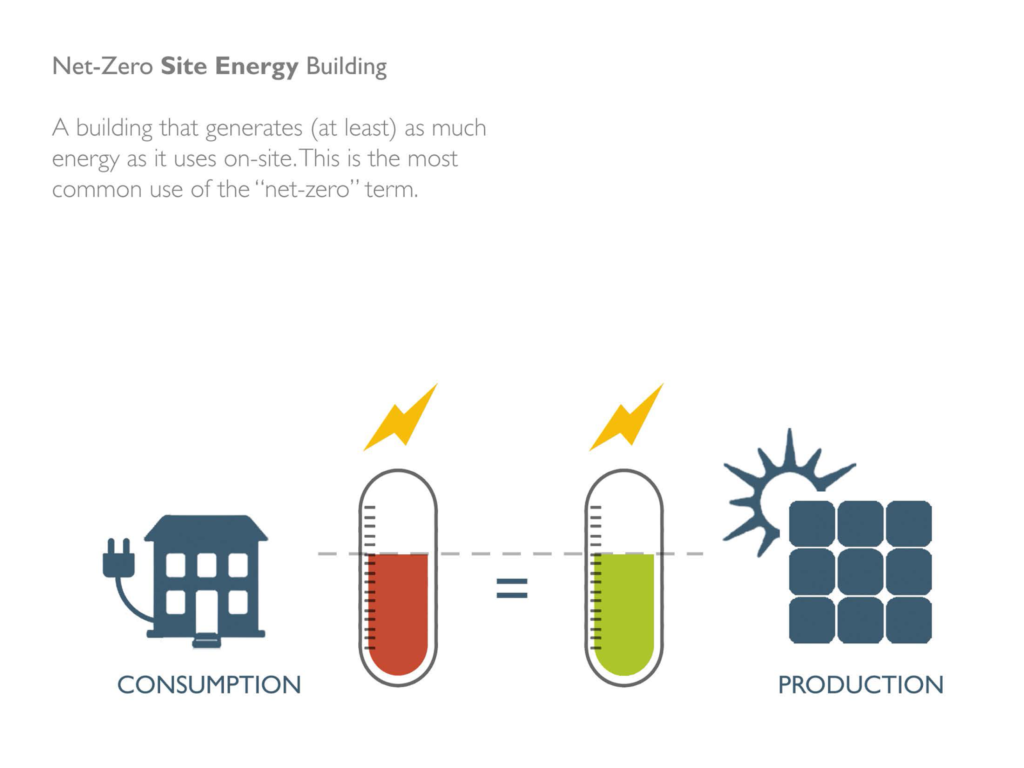
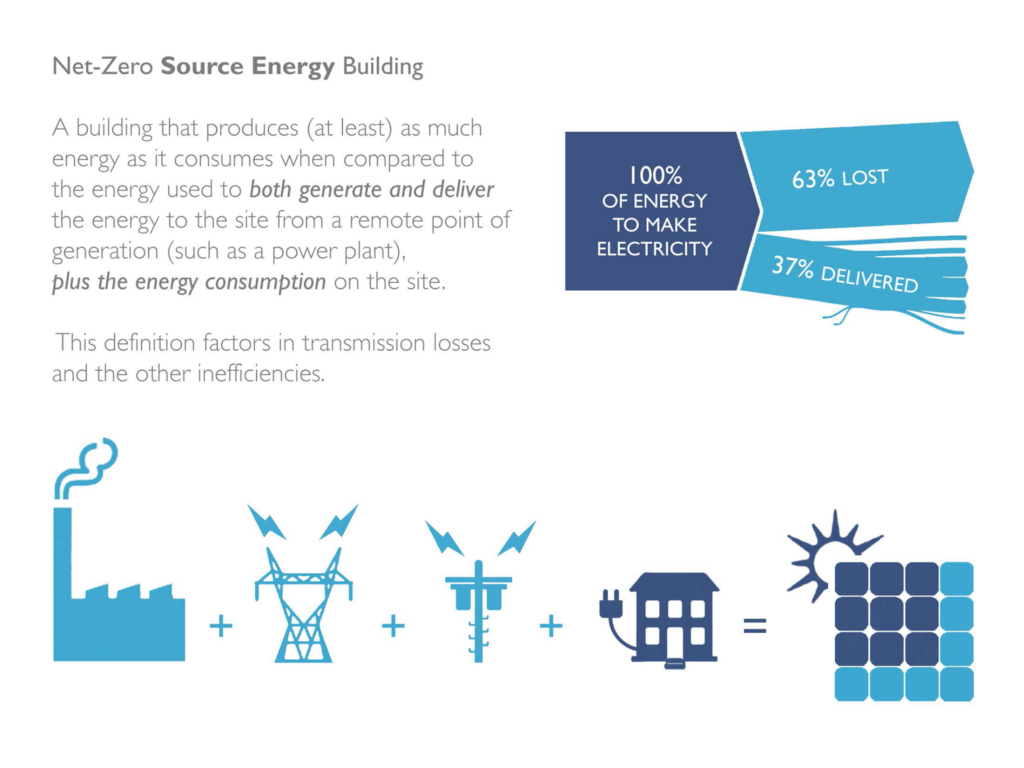
Achieving net-zero energy balance requires integrating several key strategies:
- Energy Efficiency: The first step in creating a net-zero building is reducing the overall energy demand. This can be accomplished through a combination of energy-efficient design, insulation, windows, lighting, and appliances. High-performance materials that minimize heat loss, for instance, can significantly lower heating and cooling requirements.
- Renewable Energy Generation: After minimizing energy use, the next step is to generate enough renewable energy to meet the building’s remaining energy needs. Solar panels are the most common choice, but wind turbines, geothermal systems, and bioenergy can also be used, depending on the building’s location and environment.
- Energy Storage: In some cases, renewable energy is produced in excess. Rather than allowing this surplus to go to waste, net-zero buildings often employ energy storage systems such as batteries to store energy for later use. This ensures that the building remains energy-neutral even during periods of high demand or low renewable energy production.
- Efficient Building Management Systems (BMS): To maintain optimal performance, many net-zero buildings utilize smart building technologies. These systems monitor and control various energy-consuming aspects of the building, such as lighting, heating, and cooling, ensuring that energy is used efficiently and when necessary.
Benefits of Net-Zero Buildings
Net-zero buildings offer numerous benefits, not only for the environment but also for the occupants and building owners. Some of these advantages include:
- Reduced Energy Costs: By generating their own energy, net-zero buildings reduce reliance on the grid and, in some cases, eliminate electricity bills altogether. Over time, this can result in significant financial savings.
- Enhanced Comfort: Energy-efficient design often leads to better temperature regulation and indoor air quality, improving the comfort and health of occupants. The use of natural lighting, ventilation, and high-performance insulation contributes to a more pleasant living or working environment.
- Resilience: Net-zero buildings are typically more resilient to energy price fluctuations and power outages. By relying on renewable energy sources, they are less vulnerable to changes in the energy market and can continue to operate even during grid failures.
- Lower Environmental Impact: The most significant advantage of net-zero buildings is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By minimizing energy consumption and relying on renewable energy, these buildings help reduce the construction sector’s carbon footprint, contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
- Future-Proofing: With stricter environmental regulations and energy efficiency standards on the horizon, net-zero buildings are well-positioned to meet future compliance requirements. Building owners can avoid costly retrofits and upgrades by adopting net-zero principles from the start.
Famous Examples of Net-Zero Buildings
Several net-zero buildings around the world have gained recognition for their innovative design and sustainability features. These buildings serve as models for the future of construction and highlight the possibilities of combining functionality, efficiency, and environmental responsibility.
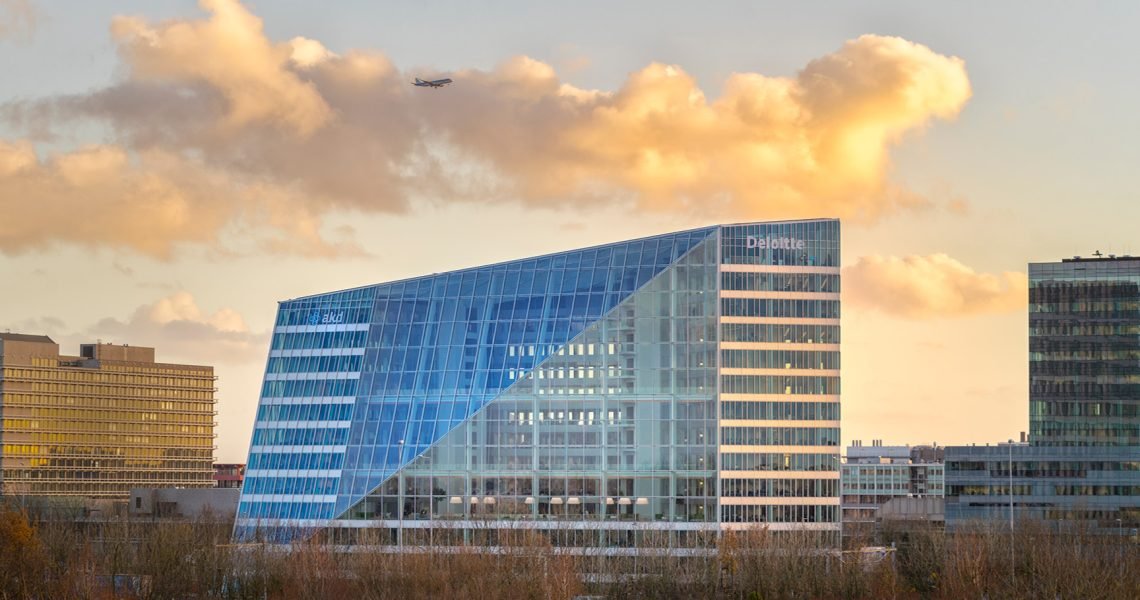
The Edge, Amsterdam
Often cited as one of the greenest and most energy-efficient office buildings globally, The Edge in Amsterdam is a cutting-edge example of net-zero construction. It uses solar panels, energy-efficient lighting, and smart building technology to achieve energy neutrality. The building also integrates rainwater collection and storage systems, further reducing its environmental impact.
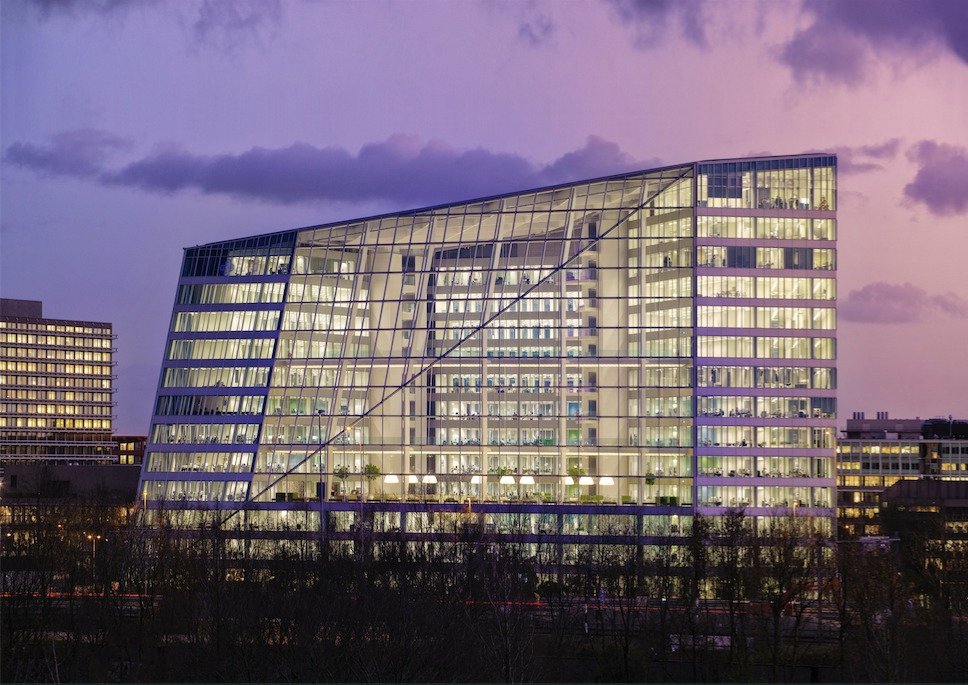
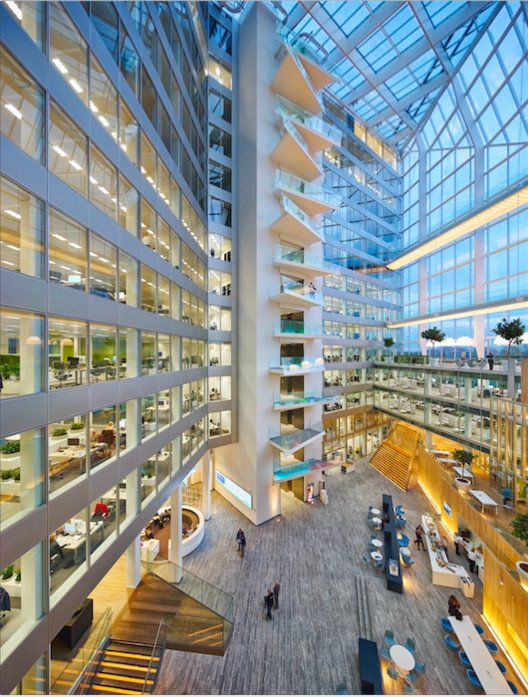


For more images of innovative net-zero designs, view The Edge by PLP Architecture.
Bullitt Center, Seattle
The Bullitt Center in Seattle is known as one of the most sustainable commercial buildings in the United States. This six-story building produces all its energy from renewable sources, including a solar array. The building’s energy efficiency is enhanced by features like natural ventilation, high-performance windows, and composting toilets. The Bullitt Center has been designed to last 250 years, making it a prime example of sustainable longevity.
The Powerhouse Kjørbo, Norway
Located in Oslo, Norway, the Powerhouse Kjørbo is a net-positive office building, meaning it generates more energy than it consumes. The building features solar panels and uses geothermal energy for heating and cooling. Its design prioritizes energy efficiency through advanced insulation and building orientation to maximize sunlight and reduce the need for artificial lighting.
Bahrain World Trade Center
The Bahrain World Trade Center is a stunning example of how renewable energy can be integrated into high-rise buildings. The two towers of this building are equipped with wind turbines that generate power for the building. This innovative design reduces the overall energy demand and sets a new standard for energy-efficient skyscrapers.
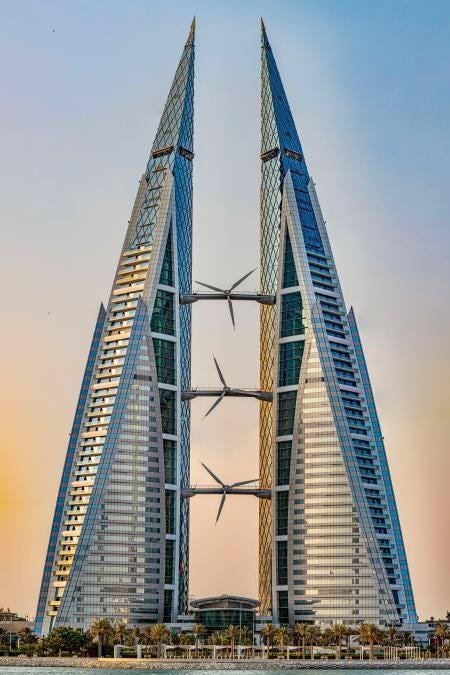
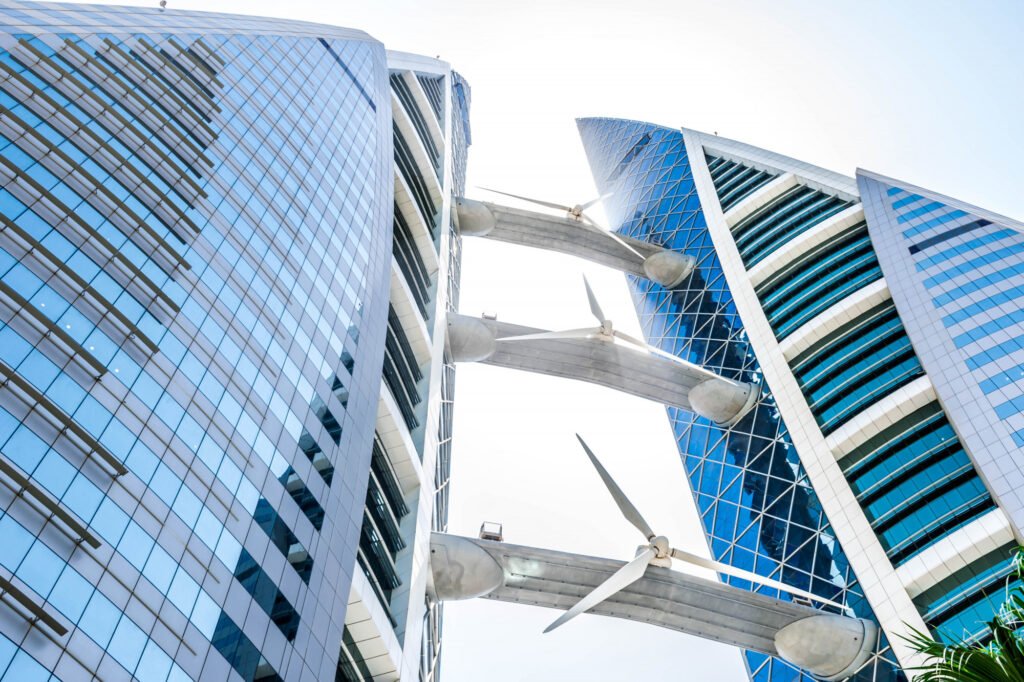
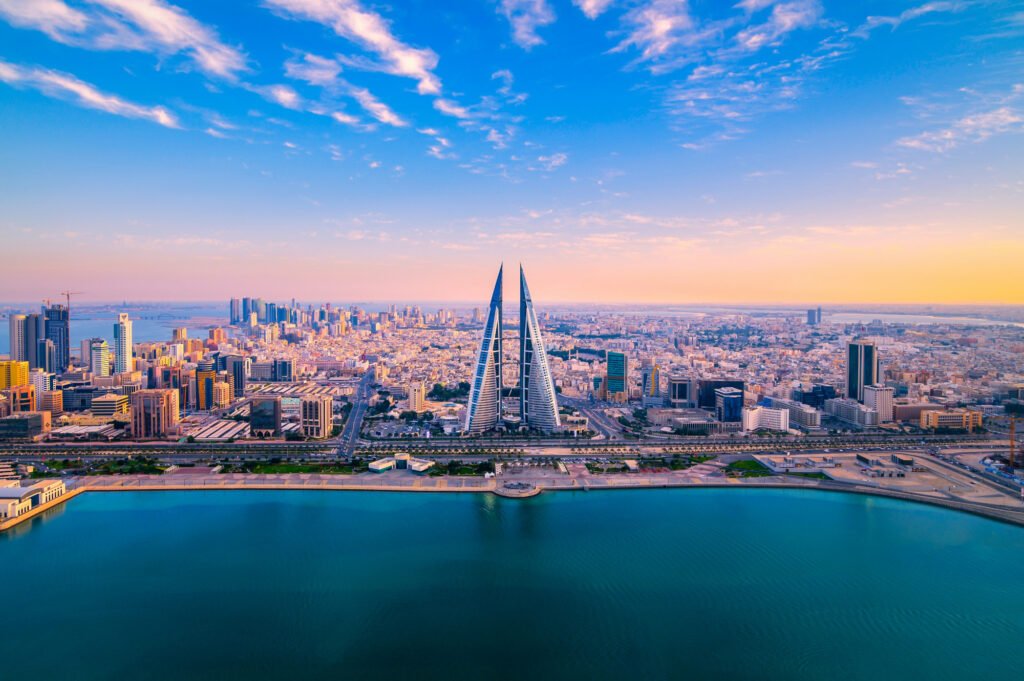



Challenges and Considerations in Net-Zero Construction
While net-zero buildings offer numerous benefits, their construction and implementation come with challenges. These challenges can vary depending on the location, building type, and available technologies. Some of the key obstacles include:
- Initial Costs: The upfront cost of designing and constructing a net-zero building can be higher than that of conventional buildings due to the need for specialized materials, renewable energy systems, and advanced technologies. However, these costs are often offset over time through energy savings and reduced operational costs.
- Technological Integration: Incorporating renewable energy systems such as solar panels, wind turbines, or geothermal systems requires careful planning and technical expertise. The success of net-zero buildings often depends on the seamless integration of these technologies into the building’s design and operation.
- Energy Storage: Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, can be intermittent, making energy storage a critical component of net-zero buildings. Advances in battery technology are helping to address this issue, but effective energy storage solutions can still be costly and complex to implement.
- Location Constraints: Not all buildings are suited to generate renewable energy on-site. For example, buildings in densely populated urban areas may have limited space for solar panels or wind turbines. In such cases, off-site renewable energy generation may be necessary to achieve net-zero status.
Conclusion
The rise of net-zero buildings marks a significant shift in the construction industry toward greater sustainability and environmental responsibility. These buildings are designed to minimize energy consumption, rely on renewable energy sources, and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Through energy efficiency measures, renewable energy integration, and smart building technologies, net-zero buildings are setting a new standard for the future of construction.
As the world continues to grapple with the impacts of climate change, the construction sector must embrace sustainable practices. Net-zero buildings offer a powerful solution to reducing the industry’s carbon footprint while enhancing energy security and resilience. The success of projects like The Edge, the Bullitt Center, and the Powerhouse Kjørbo serves as a testament to the viability and benefits of net-zero construction. These buildings not only demonstrate what is possible today but also pave the way for a more sustainable tomorrow.
At Lux Metal, we are committed to delivering high-quality, customized stainless steel solutions that meet your unique requirements while prioritizing sustainability. Whether you are working on a small DIY project or a large-scale commercial development, our team of experts is here to provide tailored solutions with precision and excellence.
Ready to take your project to the next level with innovative and sustainable metal fabrication? Contact Us to explore how our advanced facilities and expertise can bring your vision to life.
For more information on sustainability in construction and net-zero buildings, you can read these insightful articles:

