What is Compression Moulding?
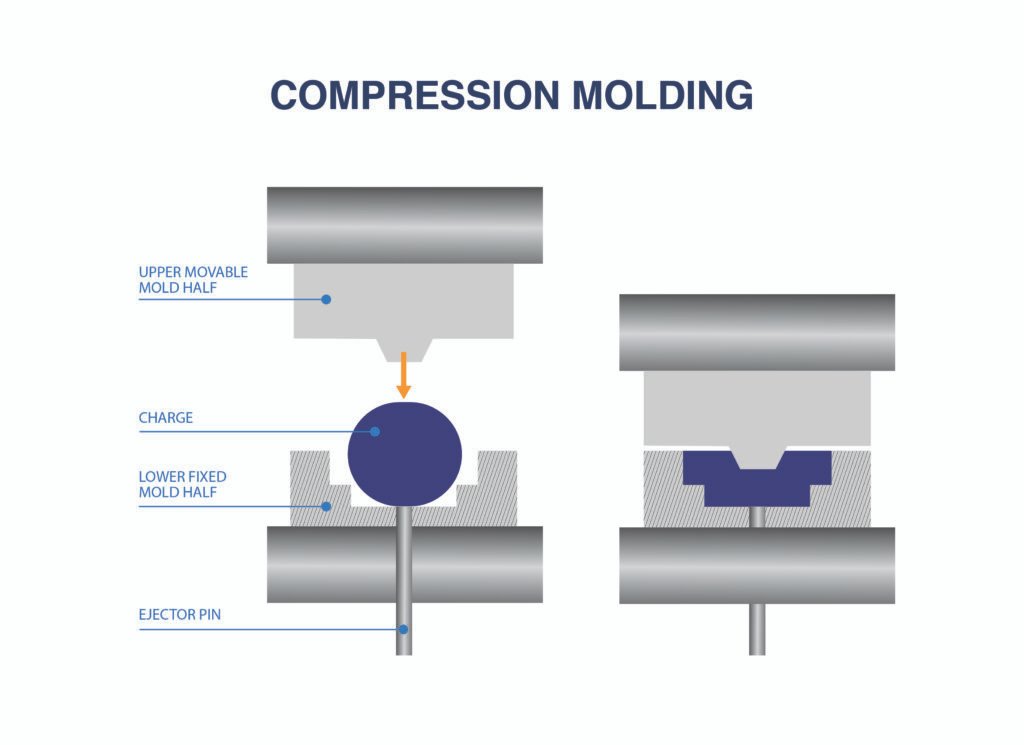
Compression moulding is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to shape raw materials into specific forms. This technique is particularly popular for thermosetting polymers, which harden when heated. While thermoplastics can also be used, the process is most commonly associated with durable, heat-resistant components.
The process involves placing a pre-measured amount of material, often in the form of granules or a preform, into a mould cavity. The mould is then closed, and heat and pressure are applied to force the material into the desired shape. Once cooled, the part is ejected from the mould, ready for further use or assembly.
Key Advantages of Compression Moulding
Compression moulding has remained relevant due to its numerous benefits:
- Cost-Effective for Large Parts:
This process is particularly economical for manufacturing large, complex components. Unlike injection moulding, it doesn’t require intricate tooling or additional clamping mechanisms, which can significantly reduce costs. - Material Versatility:
It accommodates a wide range of materials, from fiberglass-reinforced plastics to rubber compounds. This versatility makes it suitable for industries like automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. - Durability and Strength:
Compression moulding often results in products with superior mechanical properties. The uniform application of heat and pressure ensures that the material cures evenly, enhancing its structural integrity. - Reduced Material Waste:
Since the process uses pre-measured amounts of material, there is minimal wastage. Additionally, some materials used in compression moulding can be recycled, contributing to sustainable manufacturing practices. - Ideal for Prototyping and Small Batches:
Compared to other moulding techniques, compression moulding is relatively straightforward to set up, making it a popular choice for prototyping and low-volume production.
The Compression Moulding Process: Step-by-Step
- Preparation of Raw Material:
The process begins with selecting and preparing the raw material. This can be in the form of powder, granules, or preforms, depending on the application. - Heating the Mould:
The mould is preheated to the required temperature, ensuring that the material cures evenly when placed inside. - Material Placement:
A precise amount of raw material is placed into the mould cavity. Accurate measurement is crucial to avoid defects like flash or insufficient filling. - Mould Closing:
The mould is closed using hydraulic presses, applying significant pressure to compress the material into the desired shape. - Heating and Curing:
Heat is applied to the mould to cure the material. The combination of heat and pressure ensures that the material takes the shape of the mould while achieving its final properties. - Cooling and Part Removal:
Once the curing process is complete, the mould is cooled, and the finished part is ejected. Additional trimming may be required to remove any excess material or flash.
Applications of Compression Moulding
Compression moulding is widely used in various industries, thanks to its adaptability and efficiency:
- Automotive:
Components like bumpers, fenders, and interior panels are often made using compression moulding due to its ability to produce strong, lightweight parts. - Aerospace:
The method is used to create high-strength components that can withstand extreme conditions, such as structural panels and insulation parts. - Consumer Goods:
Everyday items like kitchenware, electrical housings, and handles benefit from the process’s ability to produce durable and heat-resistant products. - Industrial Equipment:
Compression moulding is also utilized for manufacturing gaskets, seals, and other critical components in heavy machinery.
Challenges in Compression Moulding
While the process has many advantages, it does come with its set of challenges:
- Longer Cycle Times:
Compression moulding typically takes longer than other methods like injection moulding due to the heating and cooling cycles. - Limited Design Complexity:
The technique is less suitable for highly intricate designs, as the material flow is more constrained compared to other methods. - Tooling Costs:
Initial mould creation can be expensive, particularly for custom or specialized designs. - Manual Processes:
Certain aspects, like material placement and part removal, often require manual intervention, which can increase labor costs.
Innovations in Compression Moulding Technology
The field of compression moulding is not static; continuous technological advancements are pushing the boundaries of what can be achieved with this versatile manufacturing process. These innovations aim to enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and open up new possibilities for product design and applications.
Advanced Materials
The development of advanced composites and bio-based materials has expanded the potential of compression moulding. Materials such as carbon fiber-reinforced plastics and biodegradable polymers are increasingly being used to create lighter, stronger, and more sustainable components. This shift aligns with growing global demand for eco-friendly manufacturing solutions.
Automation and Smart Systems
The integration of robotics and IoT (Internet of Things) into compression moulding processes is transforming production lines. Automated material loading, real-time monitoring, and precision control systems ensure consistent quality while minimizing human intervention. These smart systems also allow manufacturers to collect and analyze data, driving process optimization and predictive maintenance.
Energy-Efficient Presses
Traditional compression moulding presses consume significant energy, but newer models are designed with energy efficiency in mind. These presses use advanced heating systems, such as induction heating or localized heating zones, to reduce power consumption while maintaining performance.
3D Printing and Hybrid Techniques
The combination of compression moulding with additive manufacturing techniques, like 3D printing, is opening new doors. Hybrid approaches allow for intricate designs that were previously impossible with compression moulding alone. For example, 3D-printed preforms can be used to create complex, lightweight components with enhanced functionality.
Sustainability in Focus
Environmental considerations are driving innovations in recycling and reusing compression moulding materials. Closed-loop systems, which recover excess material during production, and the use of post-consumer recycled polymers, are becoming more common.
These advancements not only improve the efficiency and versatility of compression moulding but also position it as a forward-thinking solution for modern manufacturing challenges. For manufacturers like Lux Metal, staying updated on these innovations is essential to meet client demands and maintain a competitive edge.
Tips for Optimizing Compression Moulding
To ensure the best results, manufacturers can implement the following strategies:
- Invest in High-Quality Moulds:
Precision-engineered moulds reduce defects and improve part quality. - Regular Maintenance:
Keeping the moulds clean and well-maintained minimizes downtime and enhances product consistency. - Monitor Material Properties:
Using the right material for the application and ensuring its quality can prevent issues like warping or incomplete curing. - Optimize Heat and Pressure Settings:
Precise control of these parameters ensures uniform curing and reduces the likelihood of defects.
Compression Moulding vs. Other Moulding Methods
Compression moulding differs from other popular techniques like injection moulding and blow moulding in several key ways:
| Aspect | Compression Moulding | Injection Moulding | Blow Moulding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Use | Thermosetting polymers, thermoplastics | Primarily thermoplastics | Thermoplastics for hollow objects |
| Part Complexity | Moderate complexity | High complexity | Limited to hollow shapes |
| Setup Costs | Lower | Higher | Moderate |
| Applications | Large, durable parts | Intricate, mass-produced parts | Bottles, containers |
Future Trends in Compression Moulding
As industries shift towards sustainable manufacturing, compression moulding is also evolving. Innovations like bio-based resins and energy-efficient heating systems are making the process more eco-friendly. Additionally, advancements in automation are reducing cycle times and labor costs, enhancing overall efficiency.
For companies like Lux Metal, staying abreast of these trends is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
Conclusion
Compression moulding is a time-tested method with a wide array of applications. Its ability to produce durable, high-quality parts makes it indispensable in industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods. However, understanding its nuances and optimizing the process are critical for achieving the best results.
At Lux Metal, we specialize in delivering tailored metal solutions, leveraging cutting-edge techniques to meet our clients’ unique needs. Explore our services and learn how we can bring your ideas to life by visiting Lux Metal’s official website.
For more detailed insights into compression moulding, explore the following resources:

